There is very little information available in Chinese about CREST, the organization, and CPSA, the certification. In Taiwan, it is considered a relatively obscure certification. I gained a basic understanding of this organization and certification after reading this article: ECSA v10 Equivalent Application CREST CPSA Security Analyst Certification Tutorial / ECSA with CPSA Equivalency Recognition Step.
In December, I took the CPSA certification exam with a colleague and we both passed. I am writing this post to share my experience.
Introduction to CPSA
Let me briefly introduce CPSA, which stands for CREST Practitioner Security Analyst. It is an entry-level certification offered by CREST. The CREST series chart on the official website shows that CPSA belongs to the penetration testing category and is the most basic certification in this category:
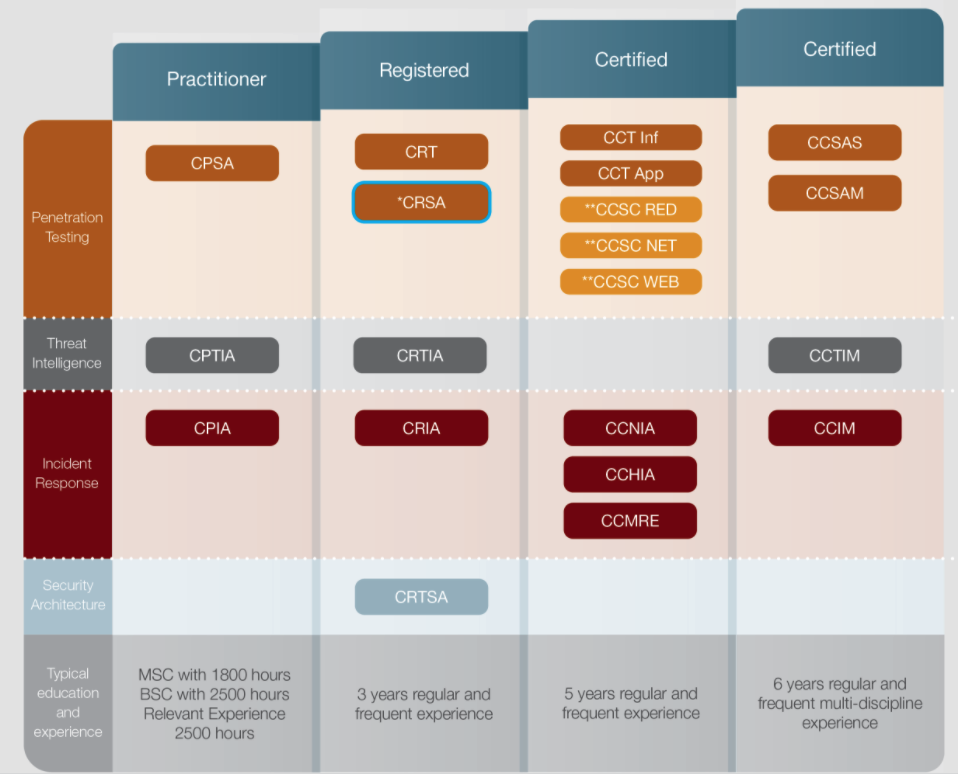
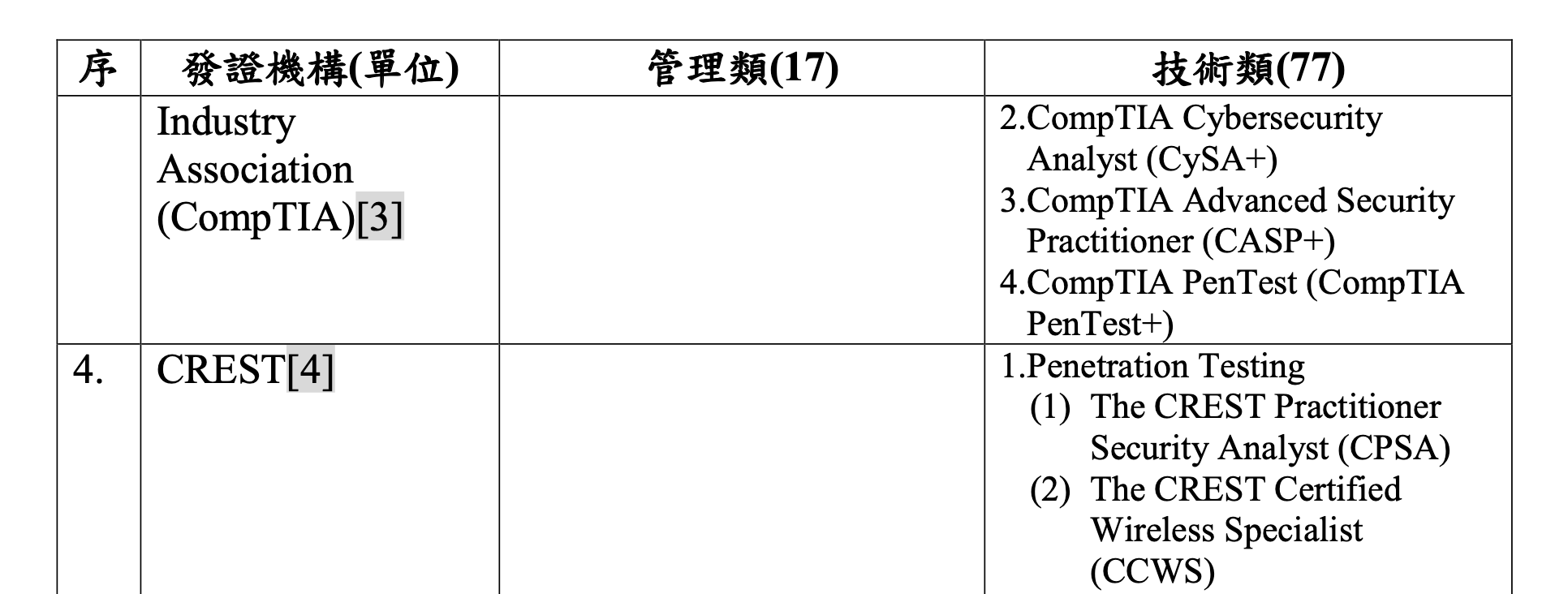
This certification is also listed in the Professional List of Information Security Certifications published by the Executive Yuan:
The official website provides the following description of CPSA:
The CREST Practitioner Security Analyst (CPSA) examination is an entry-level examination that tests a candidate’s knowledge in assessing operating systems and common network services at a basic level below that of the main CRT and CCT qualifications. The CPSA examination also includes an intermediate level of web application security testing and methods to identify common web application security vulnerabilities.
This means that CPSA is an entry-level certification that tests basic knowledge of operating systems, network security, and intermediate-level knowledge of web security. The exam consists of 120 multiple-choice questions with five options each, and candidates have two hours to complete the exam. The exam must be taken at a specific test center (Pearson Vue test centers).
CPSA Exam Content and Preparation
The CPSA official website provides a detailed outline of the exam content. However, I prefer the simplified version provided by the CPSA course, which gives a basic understanding of the exam content after a quick read:
Module 1: Soft Skills and Assessment Management
- Engagement Lifecycle
- Law and Compliance
- Scoping
- Understanding, Explaining and Managing Risk
- Record Keeping, Interim Reporting and Final Results
Module 2: Core Technical Skills
- IP Protocols
- Network Architectures
- Network mapping and Target Identification
- Filtering Avoidance Techniques
- OS Fingerprinting
- Application Fingerprinting and Evaluating Unknown Services
- Cryptography
- Applications of Cryptography
- File System Permissions
- Audit Techniques
Module 3: Background Information Gathering and Open Source
- Registration Records
- Domain Name Server (DNS)
- Google Hacking and Web Enumeration
- Information Leakage from Mail Headers
Module 4: Networking Equipment
- Management Protocols
- Network Traffic Analysis
- Networking Protocols
- IPsec
- VoIP
- Wireless
- Configuration Analysis
Module 5: Microsoft Windows Security Assessment
- Domain Reconnaissance
- User Enumeration
- Active Directory
- Windows Passwords
- Windows Vulnerabilities
- Windows Patch Management Strategies
- Desktop Lockdown
- Exchange
- Common Windows Applications
Module 6: UNIX Security Assessment
- User Enumeration
- UNIX/Linux Vulnerabilities
- FTP
- Sendmail/SMTP
- Network File System (NFS)
- R-Services
- X11
- RPC Services
- SSH
Module 7: Web Technologies
- Web Server Operation & Web Servers and Their Flaws
- Web Enterprise Architectures
- Web Protocols
- Web Markup Languages
- Web Programming Languages
- Web Application Servers
- Web APIs
- Web Sub-Components
Module 8: Web-Testing Methodologies
- Web Application Reconnaissance
- Threat Modelling and Attack Vectors
- Information gathering from Web Mark-up
- Authentication Mechanisms
- Authorisation Mechanisms
- Input Validation
- Information Disclosure in Error Messages
- Use of Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
- Use of Injection Attacks
- Session Handling
- Encryption
- Source Code Review
Module 9: Web Testing Techniques
- Web Site Structure Discovery
- Cross Site Scripting Attacks
- SQL Injection
- Parameter Manipulation
Module 10: Databases
- Databases
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle RDBMS
- MySQL
You will find that the exam content is quite extensive, covering almost everything, and a little bit of everything is tested. Therefore, at the beginning, I found it difficult to prepare and didn’t know where to focus.
So the first thing I did was to search for some English exam experience online:
- CREST CPSA Exam
- Taking the CPSA (Crest Practitioner Security Analyst) Exam
- CREST Practitioner Security Analyst (CPSA) Exam - Study Guide
The third one is the most detailed and has a lot of reference materials and resources, which I found very helpful.
Here are some directions I prepared myself:
- The full names of various proprietary terms, such as what HTTP or SSL stands for.
- Network-related knowledge, including the OSI model and protocols such as IP, TCP, UDP, and ICMP.
- Basic understanding of common encryption algorithms (such as DES, AES, and RSA) and hash functions (such as MD5 and SHA1).
- DNS-related knowledge.
- Which ports are used by common services.
Since I consider myself more familiar with web-related topics, I didn’t prepare much for that area and focused on the above topics instead.
The passing score for CPSA is 60% correct answers. My strategy was to focus on the above topics and skip the ones I found difficult or didn’t want to study. So there were some topics on the exam outline that I had never even looked at before, and I had to guess on those questions during the exam.
My main resource for preparation was not the official recommended books, which I found boring and lengthy, but rather a GitHub repository that a colleague found, which had some useful summaries of key points.
Overall, I found the exam not too difficult but a bit tedious. If you are already familiar with network-related knowledge (to the point where you can answer network-related questions in a computer science course), and have basic web knowledge, studying for a week or two should be enough to pass.
CPSA Exam
The registration fee for the exam is $400 USD, which is about NT$11,000. There seem to be only two exam centers in Taiwan, one in Taipei and one in Kaohsiung. The Taipei exam center is near the Xinyi District City Hall MRT station: https://goo.gl/maps/2hCkEpEidb8WbYQw7
You need to arrive 30 minutes early for check-in. Once you enter the exam room, you need to store all your belongings in a locker and cannot access any books or materials. So if you want to review anything, it’s best to do it outside the exam room. Then you go through the check-in process, where you need to bring your passport and a signed document (I used my credit card) and take a photo.
After that, you will be taken to the testing area, where there are many individual computer desks separated by wooden boards. You take the exam on that computer, and you can mark questions for review later.
There doesn’t seem to be a time limit for the exam, so you can submit your answers whenever you’re finished. I think I took about an hour and a half. After submitting, the exam staff will come to your seat and escort you out. You can retrieve your belongings from the locker, and they will give you a printed result sheet with your score and pass/fail status, as well as your performance in each major category.
I barely passed, but I made it. A few days later, I received the certificate from CREST.
Conclusion
Overall, I found the exam not too difficult but a bit tedious. My network knowledge is weak, so I lost some points there. If you are already familiar with network-related knowledge and have basic web knowledge, you should be able to pass the exam with some preparation.
Although the certification is not well-known in Taiwan, it has some recognition in some places abroad. If you have OSCP, you can use it to exchange for another CRT certification. For me, I just wanted to take the exam and be prepared for the future.
If you are interested, you can try taking the exam. If you have any related questions, you can leave a comment below, and I will try to answer within my ability.
Comments